Chinese Dynasties || A Beginners Guide to the History of China
Chinese Dynasties || From Han to Tang, Ming to Qing & Everything Else in Between
China is known for having a rich history, full of various fascinating rulers and inventions, but do you know in what period they happened?
Today we are going to learn about the earliest dynasties in Ancient China.
Let’s start by learning a keyword Dynasty is 王朝 wángcháo in Chinese.
Before delving into more detail like take a quick birdseye look at a general overview of Chinese history.
| Period | Time |
|---|---|
| Xia Dynasty | 2100-1600 B.C. |
| Shang Dynasty | 1600-1050 B.C. |
| Zhou Dynasty | 1050–256 B.C. |
| Qin Dynasty | 221–206 B.C. |
| Han Dynasty | 206 B.C.–220 C.E. |
| Three Kingdoms | 220–265 |
| Jin Dynasty | 265-420 |
| Period of Northern and Southern Dynasties | 386–589 |
| Sui Dynasty | 581–618 |
| Tang Dynasty | 618–906 |
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms | 907–960 |
| Song Dynasty | 960–1279 |
| Yuan Dynasty | 1279–1368 |
| Ming Dynasty | 1368–1644 |
| Qing Dynasty | 1644–1912 |
| Republic of China | 1912-1949 |
| People’s Republic of China | 1949- |
Now we are going to take a look at some of these Chinese Dynasties in a little more detail.
If you wish to skip to a particular one, click your preferred chapter here…
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Xia Dynasty
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Shang Dynasty
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Zhou Dynasty
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Qin Dynasty
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Han Dynasty
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || Other Dynasties
Ancient Chinese Dynasties || FAQ
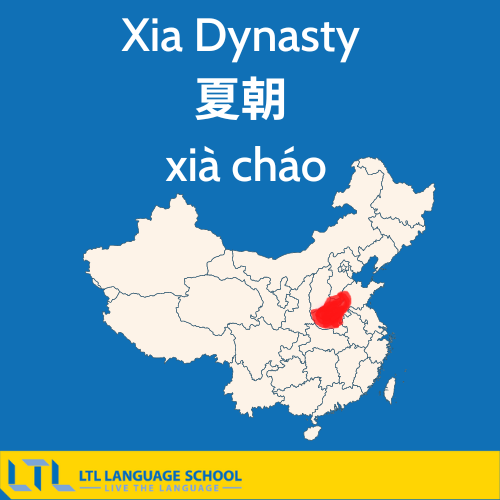
Xia Dynasty

The Xia dynasty 夏朝 (xià cháo) is considered to be mystical, as not much information was recorded about it
In fact, the first written documents discovered during the Zhou dynasty, were found over 500 years later!
Whether the Xia dynasty was actually the first Chinese dynasty is still speculated.
Due to very few documented stories, the Xia dynasty is considered to be very much like a legend.
The Xia dynasty lasted approximately from c.a. 2100-1600 B.C. with it’s founder being the legendary Yu the Great 大禹 (Dà yǔ) (c.a. 2123-2025 B.C.)
Yu was rumoured to be a descendant of the Yellow Emperor, and also the king credited with creating the method of controlling the floods and allowing agriculture to prosper.
Thanks to Yu the Great, the Xia Dynasty is believed to be the first dynasty to use irrigation and to use oracle bones.
DID YOU KNOW || Yu the Great is also said to have been assisted by a yellow dragon and a black turtle, who may have possibly been members of the Four Guardians!
BONUS || If mythology and mystery is your thing, why not check out our mammoth guide to Chinese mythology here.

The Ultimate Guide to Mythology in Chinese || 64 Mythical Beings
Discover Chinese Mythology. Learn about the 64 most fascinating mythical beings from various cultures in Chinese from our ultimate guide!
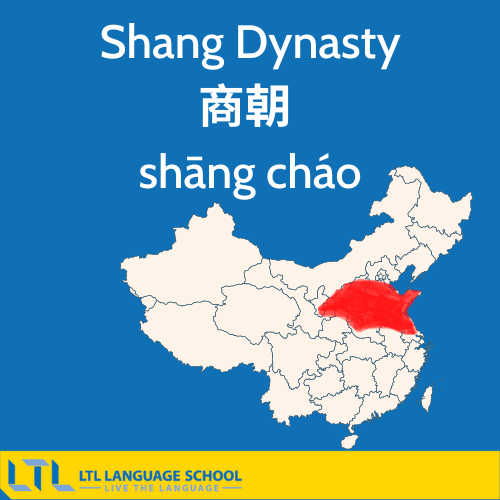
Shang Dynasty
The Xia dynasty was overthrown by the first Shang leader (Cheng) Tang 成湯 (chéng tāng) of Shang, who established the Shang Dynasty 商朝 (shāng cháo).
The Shang ruled for around 600 years from approximately 1600-1050 B.C., and during the Shang rule numerous advancements and developments were made, such as bronze technology, weaponry and writing.
Despite oracle bones being used before, the Shang were the first to develop inscriptions as a writing system – the oracle bone writing system.
BONUS CONTENT || Check out our post about the Chinese writing system to discover interesting facts and trivia!
Other than the development of the writing system, many other cultural advancements were made, such as the development of maths, astronomy, art, military strategy and musical instruments.
DID YOU KNOW || Despite musical instruments being found prior to the Shang dynasty, thanks to the bronze technology, more sophisticated instruments could be made, such as bronze drums and flutes.
BONUS CONTENT || For more interesting details about music, check out our post about the 5 must-know traditional Chinese music instruments.
Zhou Dynasty

The Zhou dynasty 周朝 (zhōu cháo) lasted approximately from 1050-256 B.C., making it the longest Chinese dynasty of almost 8 centuries!
The Zhou dynasty can be divided into 2 parts
- Western Zhou (1050-771 B.C.)
- Eastern Zhou (771-256 B.C.)
- Eastern Zhou can be divided into another 2 parts
- The Spring period
- The Autumn period
- Eastern Zhou can be divided into another 2 parts
Western Zhou first began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty and formed the Zhou dynasty, which was strong for around 75 years, but then gradually began to lose its power as in-state fighting slowly began.
After the last Western Zhou King, King You of Zhou (781-771 B.C.), was killed, the former western capital was moved from Haojing to Luoyi, which was the start of the Eastern Zhou period.
During the first half of Eastern Zhou, the Spring and Autumn period expanded not only physically (reaching the Yangtze river) but also culturally, as many schools of thought emerged such as Confucianism and Taoism, due to the relatively peaceful time allowing scholars to meet and discuss ideas.
This is why the Spring and Autumn Period became known as the time of the “Hundred Schools of Thought”.

However, the peaceful Spring and Autumn period came to an end as the nobles stopped supporting the Zhou dynasty, which lead to the states fighting among each other for power, starting the Warring States period.
During the Warring States period, 7 states fought for power; Qin, Chu, Zhao, Wei, Yan, Qi and Han.
The Warring States Period ended with the Qin victorious, partially due to Shang Yang – a reformer whose legal proposals allowed for a regulated and defined political and ruling system.
DID YOU KNOW || It was during the Warring States period that some of the greatest philosophers merged, such as Mencius, Xunzi and Han Feizi, whose different ideas influenced China significantly.
BONUS CONTENT || check out our Chinese proverbs post to learn how to speak expertly like a native
Qin Dynasty
The Qin Dynasty 秦朝 (qín cháo) lasted from 221 B.C.-206 B.C. Despite it’s relatively short rule, the Qin managed to unify all the other states, founding the very first united feudal dynasty in China!
The First Emperor of the Qin dynasty, Qin Shi Huang 秦始皇 (Qínshǐhuáng) made Xi’an the capital, which is known for the world-famous Terracotta Warriors.
Xi’an is an amazing place not only because of the Terracotta Warriors, but also as a great study location! Check out the video below for why you should study Chinese there.
Despite being known for the Terracotta Warriors, Qin Shi Huang is also known for his authoritarian and harsh reign.
DID YOU KNOW || Qin Shi Huang is infamous for executing 460 Confucian scholars and burning books and other works of literature from the Hundred School of Thoughts, excluding his Chancellor’s Li Si’s works, as Qin Shi Huang was afraid that the other novels would undermine his authority.

After surviving 3 assassination attempts, Qin Shi Huang became paranoid and obsessed with the idea of immortality, and eventually died on a trip to visit some Taoist magicians, who claimed to know where the elixir of immortality was.
After his death, Qin Shi Huang’s son, Qin Er Shi ruled for 3 years, but he was quickly overthrown by rebels led by Liu Bang, who then became the first emperor of the Han dynasty.
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty 汉朝 (hàn cháo) lasted from 206 B.C.–220 C.E., and was established by the former leader of a group of rebels, Liu Bang who became known as Emperor Gao.

The Han dynasty was considered to be the Golden Age of China, as various developments were made during this time.
The famous trading route, the Silk Road was established during the Han dynasty, with traders from various countries.
DID YOU KNOW || It is widely believed that the Romans may have traded with the traders from the Han dynasty! For a more in-depth read check out our post about Han China and the Roman Empire.
Additionally, scientific discoveries and inventions were made, such as the use of negative numbers in maths, ship rudders, paper and the seismograph (a useful tool for detecting earthquakes) which were all invented during the Han dynasty!
It wasn’t just a time of great inventions, as the economy flourished under the Han rule, with the coins issued during the Han dynaty being used all the way up to the Tang dynasty (618–907 C.E.)
However, the Han dynasty came to an end, as there were numerous conflicts with other groups, such as the Xiongnu, a nomadic group with whom the Han fought for over a century.

Eventually, several factors including internal corruption, conflicts over taxation (officials exempted themselves and the common people were weakened from the tax burden) and rebellion from religious groups who organized into military units led to the provincial governments becoming stronger than the main government.
This lead to warlordism and the Han dynasty broke into 8 regions, with the last Emperor abdicating his throne to the warlords Cao Cao son, Cao Pi, ending the Han dynasty and creating the time period known as The Three Kingdoms.
Other Dynasties
Let’s take a quick overview of the other Chinese Dynasties too.
Three Kingdoms (220–265) 三国 (sānguó) was made up of the Kingdoms of Shu, Wei and Wu.
The wars between these rival kingdoms ended up causing damage to the development of the Kingdoms, eventually leading to the Wei Chancellor Sima Yan overtaking the Kingdoms and founding the Jin Dynasty.
Jin Dynasty (265-420) 晋朝 (jìncháo) was a dynasty made up of Western Jin (266–316) and Eastern Jin (317–420).
The Eastern Jin Dynasty eventually fell as it was weakened by civil wars, and completely overthrown by a General Liu Yu in 420, starting the Liu Song dynasty, the first Dynasty of the Period of Northern and Southern Dynasties.
Despite the Period of Northern and Southern Dynasties (386–589) being strongly politically divided, it was also an age of great inventions and scientific advancements in maths, medicine and astronomy.
The Northern Dynasties were made up of Northern Wei, Western and Eastern Wei, Northern Zhou and Northern Qi, with the Southern Dynasties being Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang, Chen and Western Liang.
Ultimately, Sui forces captured the Chen capital and the Chen emperor, Chen Shubao, and started the Sui Dynasty.
The Sui Dynasty (581–618) managed to unite the Northern and Southern dynasties together, with various reforms improving agriculture and trade networks.
Unfortunately the Sui Dynasty fell, as the Sui Dynastys’s Emperor Yang was assassinated, leading to revolts and civil war, as Emperor Yang’s conscripted labour and heavy tax reforms were rather unpopular.

The Tang Dynasty (618–906) was known for its strong military power, great diplomatic relations, artistic and literary works.
The Tang Dynasty came to an end when Zhu Wen, a strong military governor, overthrew the Emperor’s son, establishing Later Liang, the first Dynasty of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) was a politically unstable time, as there was constant fighting among the rulers and warlords for power, as each ruler wanted to control the entire area of the former Tang Dynasty.
This period ended with a General Zhao Kuangyin staging a coup and founding the Song Dynasty in 960.
The Song Dynasty (960–1279) had conflicts with the Northern dynasties, but was still a period of great achievements, such as the inventions of gunpowder and the very first banknotes.
To fight against the Jin, the Song Dynasty united with the Mongols, who eventually ended up turning on their ally, the Song, leading to Kublai Khan becoming the Khan and creating the Yuan Dynasty.
The Yuan Dynasty (1279–1368) was the first foreign-ruled dynasty, with various cultural developments being made, such as the famous classical chinese novels “The Romance of the Three Kingdoms” and “Water Margin” being written.
The local people suffered from constant natural disasters, and due to the governments lack of support this resulted in an uprising against the Yuan, and with the weakened Yuan forces, the Ming comfortably ended the Yuan Dynasty.
The Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) was famous for the construction of the Forbidden City, and the rise of the beautiful blue and white porcelain.
Due to corruption among officials and poor living conditions for the common people, a rebellion was launched and won by Li Zicheng against the Ming Dynasty, who was in turn defeated by the Manchurian army, who seized Beijing and established the Qing Dynasty.
The Qing Dynasty (1644–1912) was the final imperial dynasty in the Chinese history.
The Qing Dynasty was overthrown by a revolution in 1911, as internal conflicts weakened the dynasty’s power. The last Emperor abdicated in 1912, ending the dynasties and starting a new era in the Chinese history; The Republic of China.
The Republic of China (1912-1949) is known for being a founding member of the League of Nations, which later became the United Nations.
After the Chinese Civil War between the Kuomintang, a Chinese Nationalist Party and the Chinese Communist Party, Mao Zedong’s communist party won, establishing the modern-day People’s Republic of China.
As you can see, Chinese history is deep and with so much to cover, we can only skim the surface in this article today.
Hopefully though, we’ve taught you plenty about the historic dynasties of China.
Tell us what you think in the comments below and feel free to ask any questions.
Chinese Dynasties || FAQs
What were the 5 earliest dynasties in Chinese history?
The 5 earliest Chinese dynasties were Xia, Shang, Zhou, Qin and Han.
Why is the Xia dynasty considered to be mythical?
Because not a lot of information was recorded about it.
The first written documents about the Xia dynasty were discovered over 500 years later.
Into what parts can the Zhou dynasty be divided?
Western Zhou, Eastern Zhou, Spring and Autumn and the Warring States.
What city did Qin Shi Huang make the capital, and what is it famous for?
Xi’an, which is most famous for the Terracotta Warriors.
You can study Chinese in Xi’an with us at LTL too!
What dynasty was considered to be the Golden Age in the Chinese history?
The Han dynasty 汉朝 (hàn cháo) which lasted from 206 B.C.–220 C.E.
It was established by the former leader of a group of rebels, Liu Bang who became known as Emperor Gao.
Want more from LTL?
If you wish to hear more from LTL School why not join our mailing list.
We give plenty of handy information on learning Chinese, useful apps to learn the language and everything going on at our LTL schools.
FANCY SOME FREE ONLINE LESSONS? Grab a free 7 day trial and come and see why our LTL Flexi Classes are taking language learning to a whole new level.
Sign up below and become part of our ever growing community!
![[𝗢𝗟𝗗] LTL Beihai Logo](https://old.ltl-beihai.com/wp-content/sites/17/logo-ltl-header.png)

 Hi, my name is Mojca! I am from Slovenia in Europe and I work as a student advisor at our Shanghai school.
Hi, my name is Mojca! I am from Slovenia in Europe and I work as a student advisor at our Shanghai school.


2 comments
[…] For more on Chinese history, check out our beginner’s guide to Chinese Dynasties! […]
[…] Want to learn more about Chinese history? Check out our Beginner Guide to Chinese Dynasties here! […]